Why Is Documentation Important In Software Development
February 20, 2024
How to Plan Out Your Software Development Journey
February 4, 2025
Table of contents
- Introduction
- 1. Understanding WordPress
- 2. Setting up your domain and hosting
- 3. Installing WordPress
- 4. Navigating the WordPress Dashboard
- 5. Choosing and installing a theme
- 6. Essential plugins for your website
- 7. Creating content
- 8. Customising your website
- 9. Managing users
- 10. Maintaining your WordPress site
- Conclusion
Introduction
Welcome to a step-by-step guide on getting started with WordPress! Whether you’re creating a personal blog, a business website, or an online store, WordPress is a powerful and flexible platform that can help you achieve your goals. In this guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know to get your WordPress site up and running.

1. Understanding WordPress
What is WordPress?
WordPress is a free, open-source content management system (CMS) that powers over 40% of all websites on the internet. It’s known for its user-friendly interface and flexibility.
What is the difference between WordPress.com and WordPress.org?
- WordPress.com: A hosted solution where WordPress handles hosting and maintenance. Suitable for beginners who don’t want to worry about technical aspects.
- WordPress.org: A self-hosted solution where you have full control over your site. You’ll need to purchase hosting and manage your own updates and backups.
What are the benefits of using WordPress?
- Easy to use, even for beginners.
- It can be more affordable than most other CMS programs.
- Highly customisable.
- Plenty of themes and plugins to choose from.
- Large community.
- Documentation and extensive resources are available.

2. Setting up your domain and hosting
What is a domain name?
Your domain name is your website’s address on the internet (e.g., www.yourwebsite.com). Choose something short, memorable, and relevant to your brand. To check whether your domain name is available, click here.
What is a web host or hosting provider?
Hosting is where your website’s files are stored. Web hosting is usually comprised of a server, a domain name, and a hosting provider. You need web hosting in order to make your website accessible via the World Wide Web. Look for a provider that offers good performance, reliability, and support.
Popular options include:
- DirectCloud
- Bluehost
- HostGator
- SiteGround
- Axxess
- InMotion Hosting
- Xneelo
- Domains.co.za
- HostAfrica
- WP Engine
- Kinsta
- 1-Grid
Steps to purchase and set up hosting
- Sign up for a hosting plan.
- Register your domain name (often included with hosting plans).
- Set up your hosting account and connect your domain.

3. Installing WordPress
One-click installation via web host provider
Many hosting providers offer a one-click installation process for WordPress. Log in to your hosting account, find the WordPress installer, and follow the prompts.
Manual installation process
- Download the WordPress software from WordPress.org.
- Upload the files to your hosting account via FTP.
- Create a MySQL database and user.
- Run the WordPress installation script.
Initial setup
- Choose your site title and tagline.
- Create an admin account with a strong password.
- Select your preferred language and time zone.
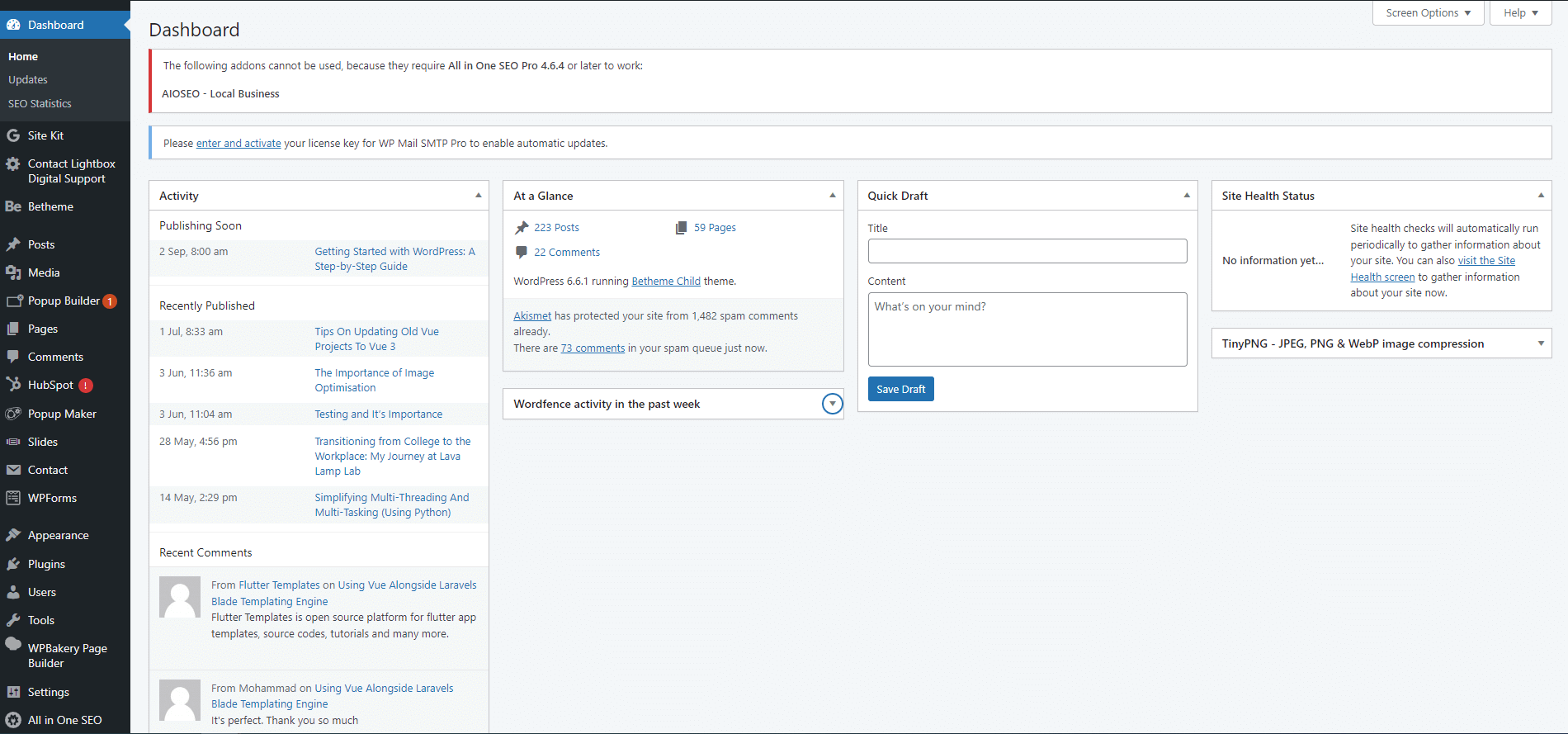
4. Navigating the WordPress Dashboard
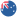
Overview of the WordPress Dashboard interface
The WordPress dashboard is your control panel for managing your site. Familiarise yourself with the layout and menu options.
Key sections
- Posts: Manage blog posts.
- Pages: Manage static pages.
- Media: Upload and manage images, videos, and other media.
- Comments: Moderate comments from visitors.
- Appearance: Customize your site’s look and feel.
- Plugins: Add and manage plugins.
- Users: Manage user accounts and permissions.
- Tools: Import/export content and other tools.
- Settings: Configure site settings.
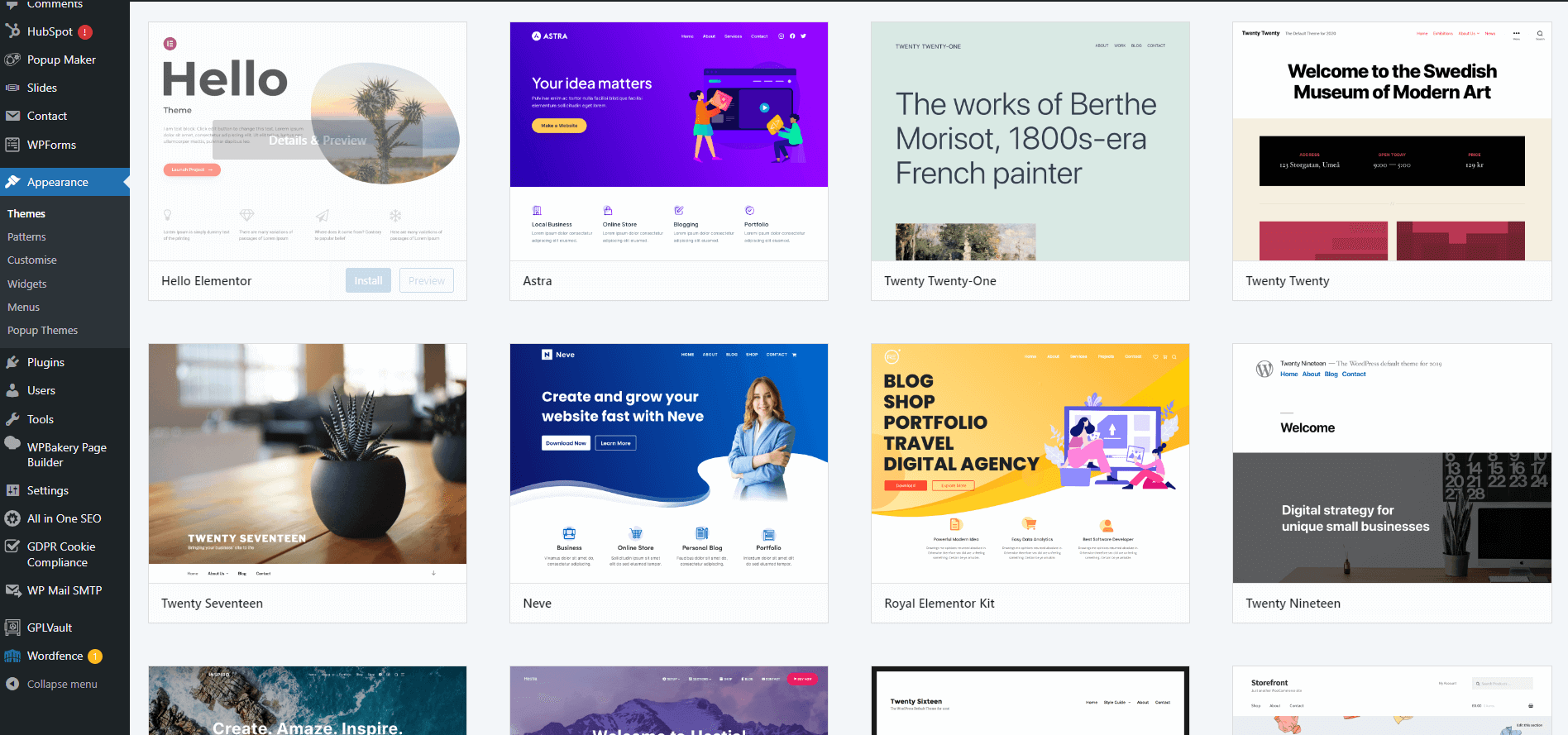
5. Choosing and installing a theme
Browsing and selecting a theme
The WordPress theme repository offers thousands of free themes. You can also purchase premium themes from marketplaces like ThemeForest. It is advisable that you purchase a paid theme as free themes are often limited in capabilities.
Installing a free theme from the WordPress repository
- Go to Appearance > Themes > Add New.
- Browse or search for a theme.
- Click “Install” and then “Activate.”
Uploading and installing a premium/paid/pro theme
- Purchase and download the theme.
- Go to Appearance > Themes > Add New > Upload Theme.
- Choose the theme file and click “Install Now.”
- Click “Activate.”
Customising your theme
Use the Customizer (Appearance > Customise) to adjust settings like logos, colors, fonts, and layout. Some themes have additional customization options. Some themes will have their own section for customisation.
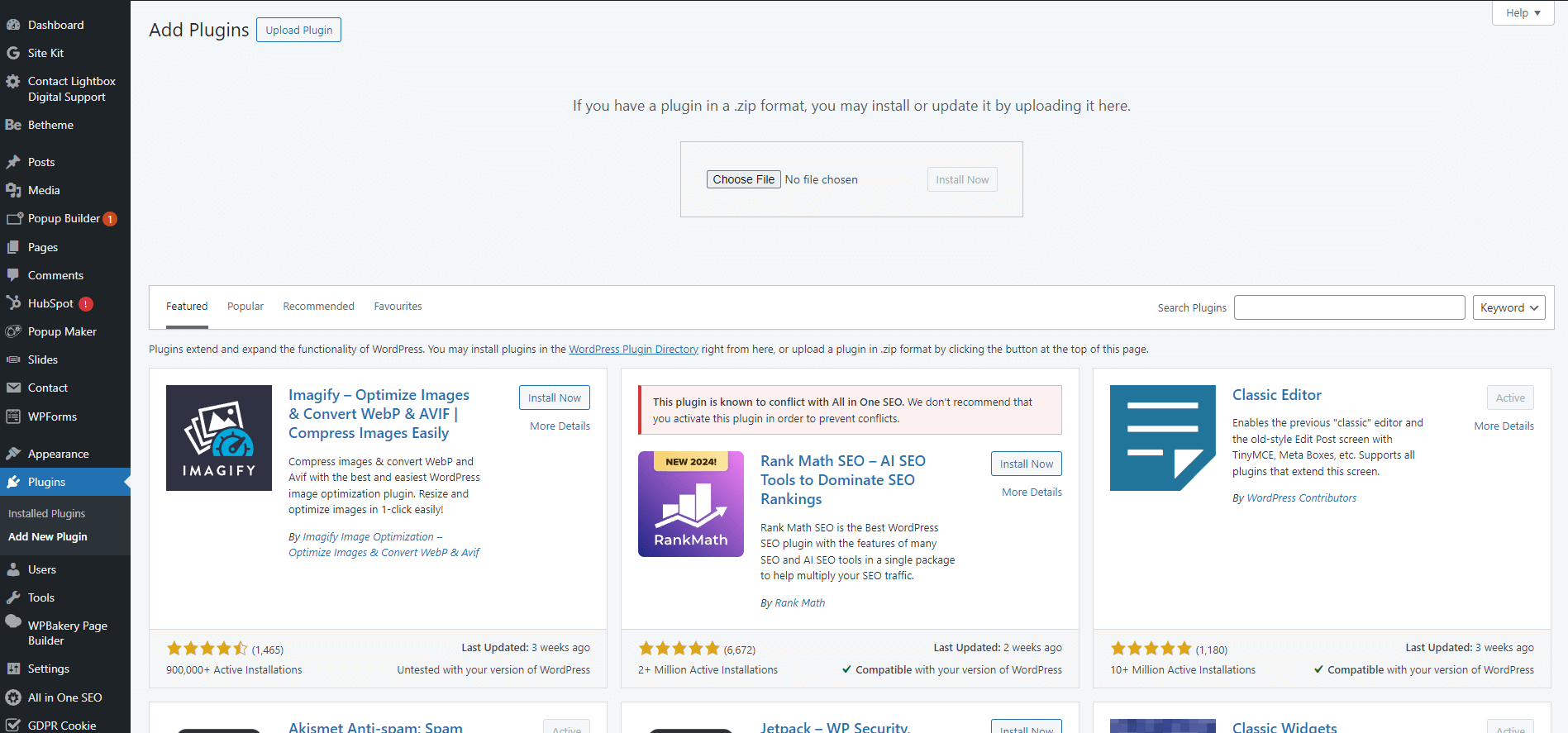
6. Essential plugins for your website
Explanation of plugins
Plugins extend the functionality of WordPress. There are thousands of plugins for all sorts of things like SEO, security, backups, performance, and more. Plugins can be free or a once-off cost, monthly cost, or yearly cost. It all depends what you need and are looking for and to what level of customisation you need.
Recommended plugins
- Security: Wordfence, Sucuri.
- SEO: Yoast SEO, All in One SEO, Rank Math.
- Backups: UpdraftPlus, SolidBackups.
- Performance: W3 Total Cache, WP Super Cache, WP Rocket.
- Social media: Social Snap, Monarch.
How to install and activate plugins
- Go to Plugins > Add New.
- Browse or search for a plugin.
- Click “Install Now” and then “Activate.”
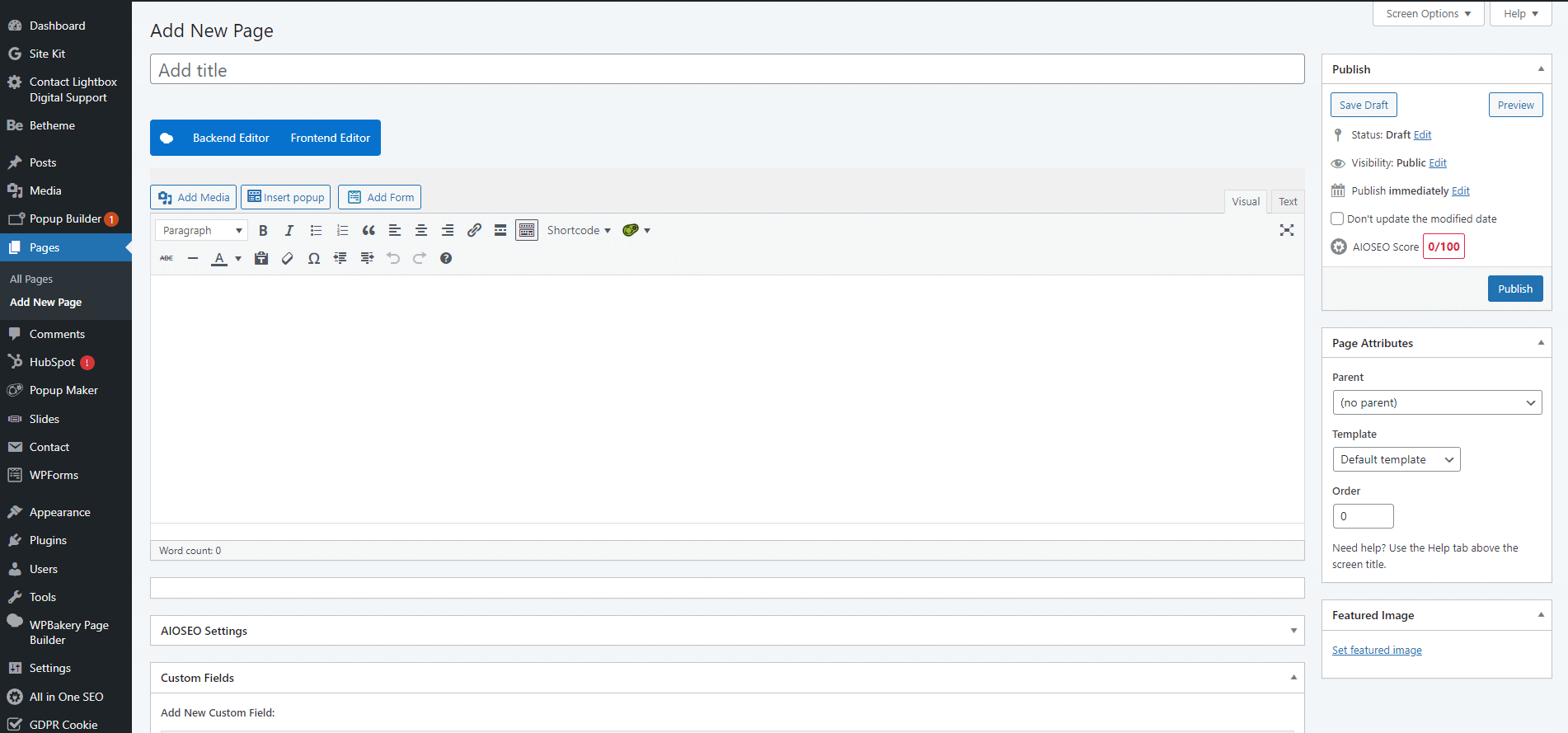
7. Creating content
Posts vs. Pages
- Posts: Blog entries that are displayed in reverse chronological order.
- Pages: Static content like About, Contact, and Home.
Creating and publishing a new post
- Go to Posts > Add New.
- Enter a title and content.
- Add categories and tags.
- Set a featured image.
- Click “Publish.”
Creating and publishing a new page
- Go to Pages > Add New.
- Enter a title and content.
- Customize the page template (if available).
- Click “Publish.”
Using categories and tags
- Categories: group related posts together. Example: a house, car.
- Tags: describe specific details. Example: windows, door, paint, wheels, gearbox
Tips for writing and formatting content
- Use headings, bullet points, and short paragraphs.
- Include images and media to enhance your content.
- Optimise for SEO by including keywords and meta descriptions.
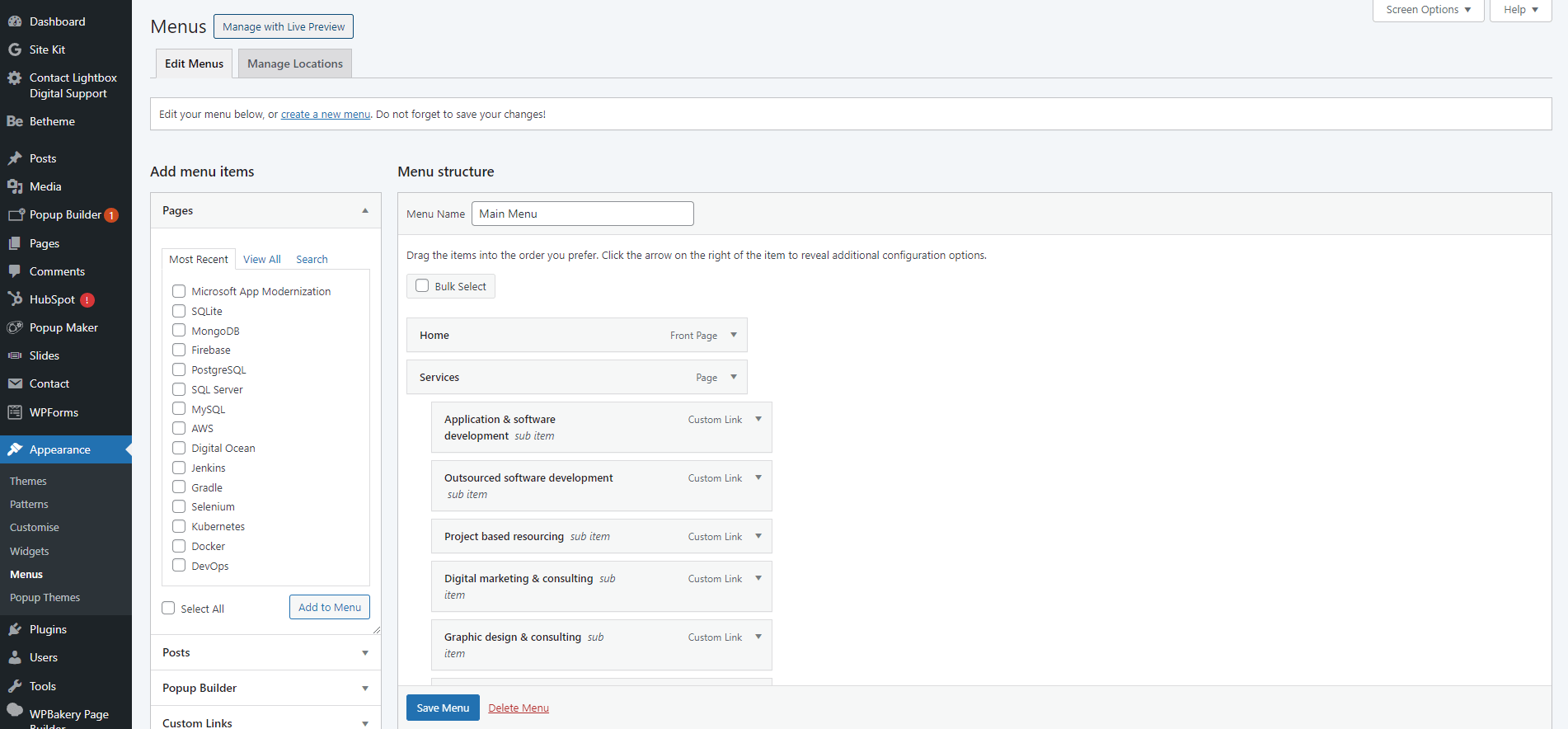
8. Customising your website
Setting up a custom menu
- Go to Appearance > Menus.
- Add pages, posts, categories, and custom links to your menu.
- Organize menu items with drag and drop.
- Assign the menu to a location (e.g., primary, footer).
Adding Widgets to Your Sidebar and Footer
- Go to Appearance > Widgets.
- Drag and drop widgets into the desired widget areas.
- Customize widget settings.
Customising Your site’s appearance with the Customizer
- Go to Appearance > Customize.
- Adjust settings for site identity, colors, fonts, layout, and more.
Creating a static front page
- Go to Settings > Reading.
- Select “A static page” and choose your homepage and blog page.
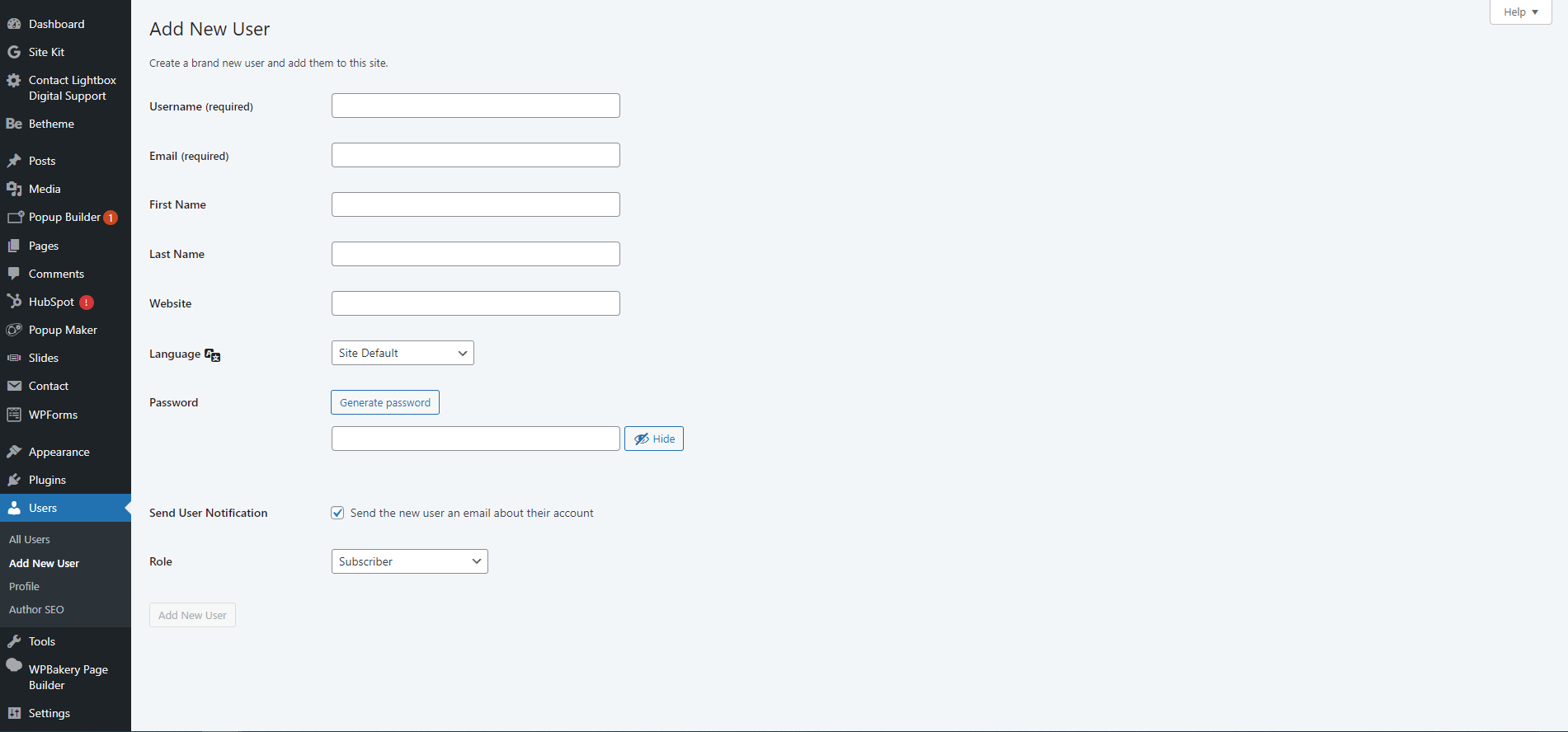
9. Managing users
Adding and managing users
- Go to Users > Add New.
- Enter user details and select a role.
- Click “Add New User.”
Understanding user roles and permissions
- Administrator: Has full control over the site.
- Editor: Can manage content and moderate comments.
- Author: Write and publish their own posts.
- Contributor: Write but do not publish their own posts.
- Subscriber: Manage their own profile.
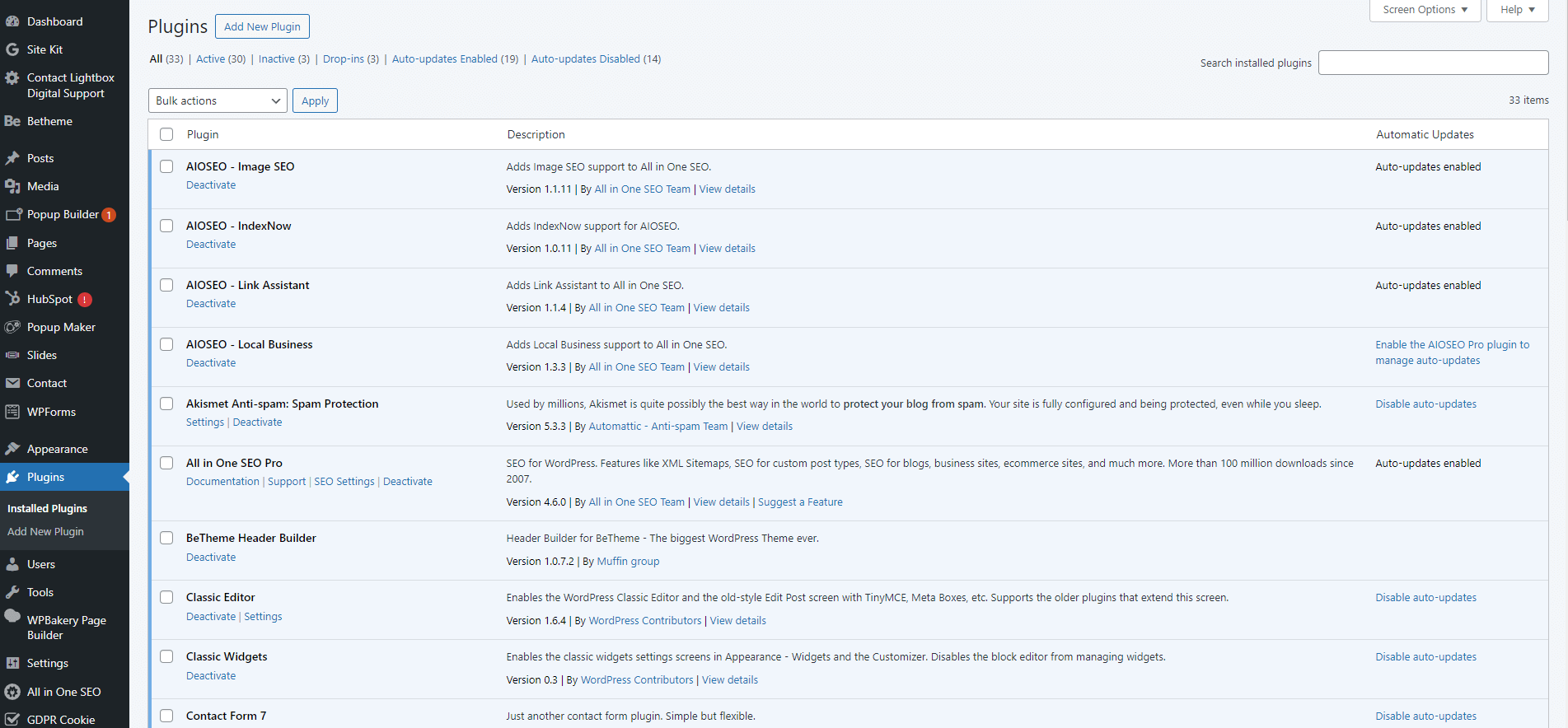
10. Maintaining your WordPress site
Updating WordPress core, themes, and plugins
- Regularly check for updates (Dashboard > Updates).
- Always back up your site before updating.
Regular backups and security checks
- Schedule automatic backups with a plugin.
- Perform security scans and monitor for vulnerabilities.
Monitoring site performance
- Use tools like Google Analytics and MonsterInsights to track traffic and performance.
- Optimise images and enable caching to improve load times.
If you need a company to help maintain your website, don’t hesitate to contact us.

Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve taken the first steps toward creating your own WordPress website. Remember, the key to success is continuous learning and experimentation. As you become more comfortable with WordPress, don’t hesitate to explore advanced features and customization options. For further learning, check out the WordPress Codex, forums, and online courses.
By following this guide, you’ll have a solid foundation to build and manage your WordPress site. Happy blogging!