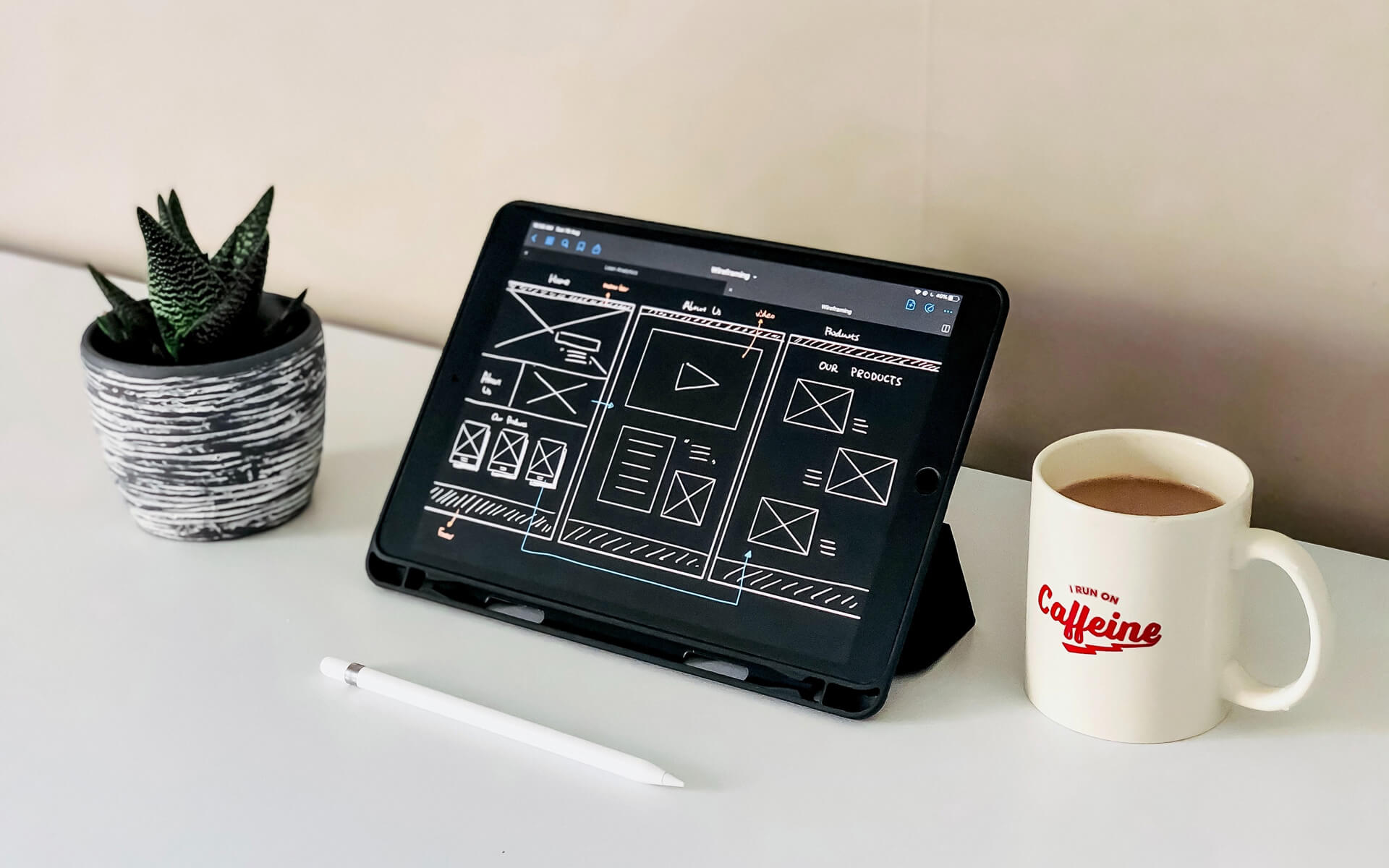
The Art Of Wireframes & Mock-Ups
October 7, 2021
Slider Revolution Plugin For WordPress
October 22, 2021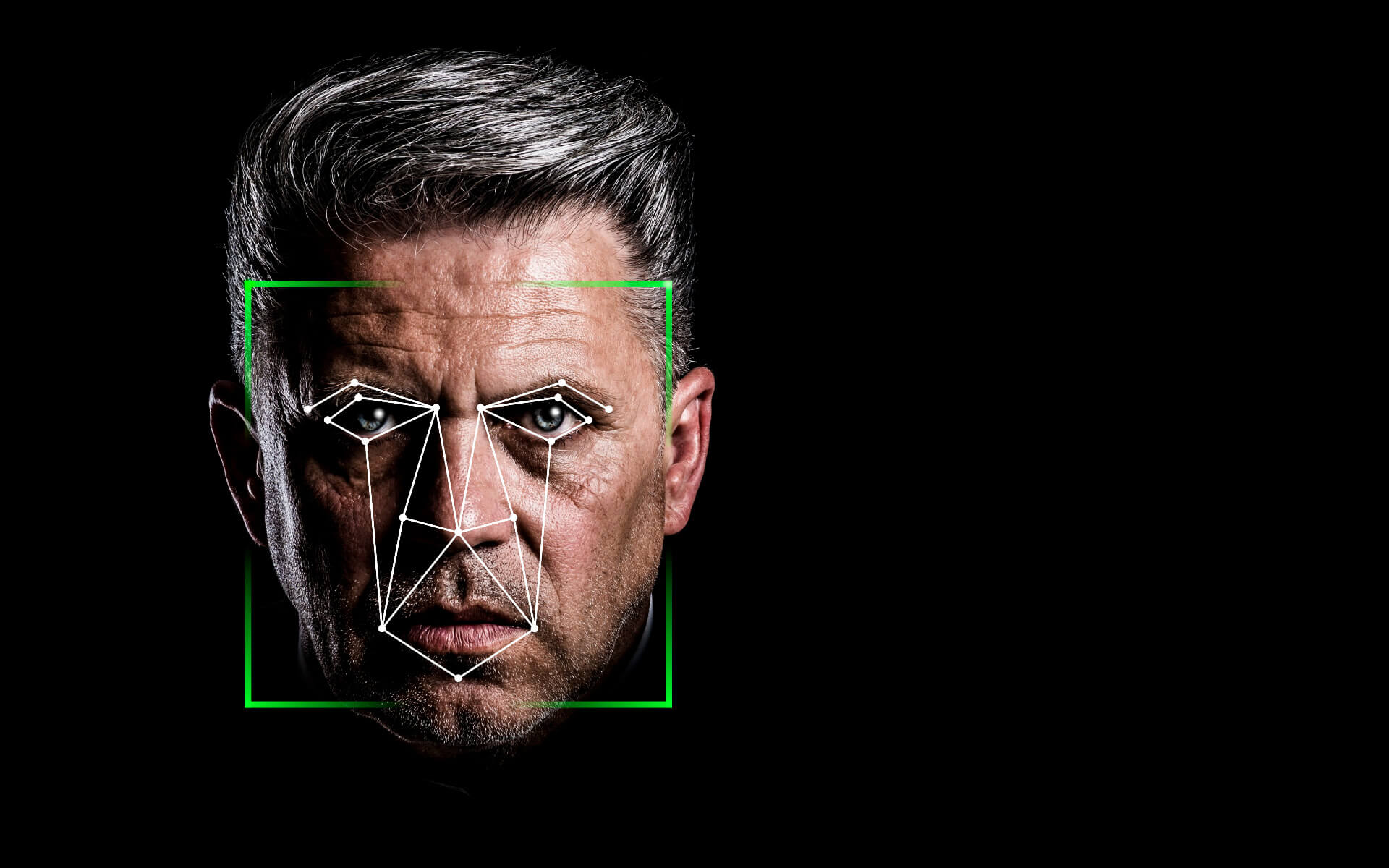
Computer vision is a field of computer science focused on replicating parts of the complexity of human vision systems and enabling computers to detect and process objects in images and videos in the same way humans do. One of the most prominent applications is in the medical computer visualization field where medical image processing is characterized by the extraction of information from image data to diagnose patients. Computer visualisation systems process images from satellites, drones and aircraft to identify early-stage problems and avoid unnecessary financial losses.
To get the most out of the image data, we need a computer to see the images and understand the content. We train the computer with huge amounts of visual data computers to process images, label objects in them and find patterns in them. For example, when sending a million images of flowers, the computer analyzes the images to identify patterns similar to those of flowers, and at the end of the process creates a model and as a result is able to recognize a particular image of a flower every time we send it an image.
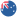
The classic problem with image processing is to determine whether or not the image data contains certain objects, features, or activities. Computer Vision, at its core, is focusing on the design of computer systems capable of capturing, understanding and interpreting important visual information in pictures and video data. Computer-visual systems translate this visual information using contextual knowledge to provide people with insights that can be used to make decisions. A task of computer vision involves the capturing, processing, analyzing and understanding of digital images, as well as extracting high-dimensional data from the real world to produce numerical and symbolic information.
One way to train computers to understand visual data is to send images (many images with thousands or even millions of possible captions) and subject them to different software techniques and algorithms that allow them to search for patterns and elements related to the images. For example, if you feed a computer a million images of cats (because we all love cats) and the computer subjects the images to an algorithm that allows the images to analyze the colour of the photos, the shape and distance and the shape of objects borders among other things, the computer can see what each profile means.
Image processing is a type of digital signal processing that is not about understanding the content of the image. Due to the specific nature of images, many computer vision methods have been developed that correspond to the processing of one variable signal into another. Any computer image processing system requires image processing to apply to the raw data.
Computer vision has a variety of applications - from the old (mobile robots for navigation, industrial inspection and military intelligence ) to the new (human - computer interaction, image restoration, digital libraries, medical image analysis, realistic reproduction of synthetic scenes and computer graphics ). Computer vision can solve complex problems such as facial recognition (for example, through use of filters), detailed image analysis (which enables visual searches for Google images) and biometric identification methods. Computer vision is not only adept at recognizing elements and objects in digital images, but, in contrast to humans, can also recognize patterns that are missing in the human visual system.
One of the recent applications of computer vision is in the virtual reality explosion. By the processing of images and video streams it has become possible to create basic object tracking through methods such as colour filtering and contour definitions. Colour filtering involves removing specific colours from an image where then the remaining colours have contours applied. Contour in computer vision is the process where the noticeable differences from one colour to another, usually denoting an object's edge, is found and further highlighted, which can solve the previously mentioned issue of knowing what is and is not an object in an image.
An example would be an image of a blue gloved hand, palm facing the camera and fingers spread out, against a red background. Computer vision systems would be capable of determining where the hand starts and the wall begins. By first extracting only blue pixels and all other pixels are set to black. Then the blue pixels are all made white, eventually ending on a white hand silhouette on a black background. Here contours can be found by scanning an image to determine the pixels that make up the hand in better detail, possibly even some clever computer vision processes can be further applied to identify the individual digits.
If one can identify the individual digits of a hand, frame by frame, and track the movement each digit has made from each frame then virtually the gesture of the hand is known. Gesture control is another outcome of computer vision, the wave of a hand to swipe left and right, the pinch of the fingers to increase and decrease volume, the clasping of the fist to grab something in a virtual space.
Other fantastic applications of computer vision have assisted with lessening the travel restrictions caused by the Covid-19 pandemic. The process of homography in the computer vision family of techniques and processes is the process of mapping one image plane, a flat surface with no curves, to another based on features within those images. An example would be a picture frame on a white wall. At each corner of the frame is a blue square and the actual contents of the picture frame is transparent, showing the white wall. By applying homography to the described scenario an image can be overlayed into the picture frame in our virtual world. This can even be applied to videos, ultimately creating moving pictures.
There are some art gallery projects which apply homography to create a virtual viewing space for customers, all from the comfort of the home. Another not well known application of homography is the advertisement industry. A sports event viewed online could show relevant advertisements which are placed onto the real world match field, allowing any advert to be seamlessly displayed without any physical interaction with the field..
Whether identifying what is a fire hydrant in an image for google smart cars, following hand gestures or creating virtual art galleries, computer vision has been indispensable in many real world applications to our lives, whether we know where and how or not. As computers become smarter, faster and newer more efficient methods of processing images arise, computer vision will explode every time to more and more applications to benefit lives.