Power BI
August 5, 2021
UX Consistency In Web Development
August 20, 2021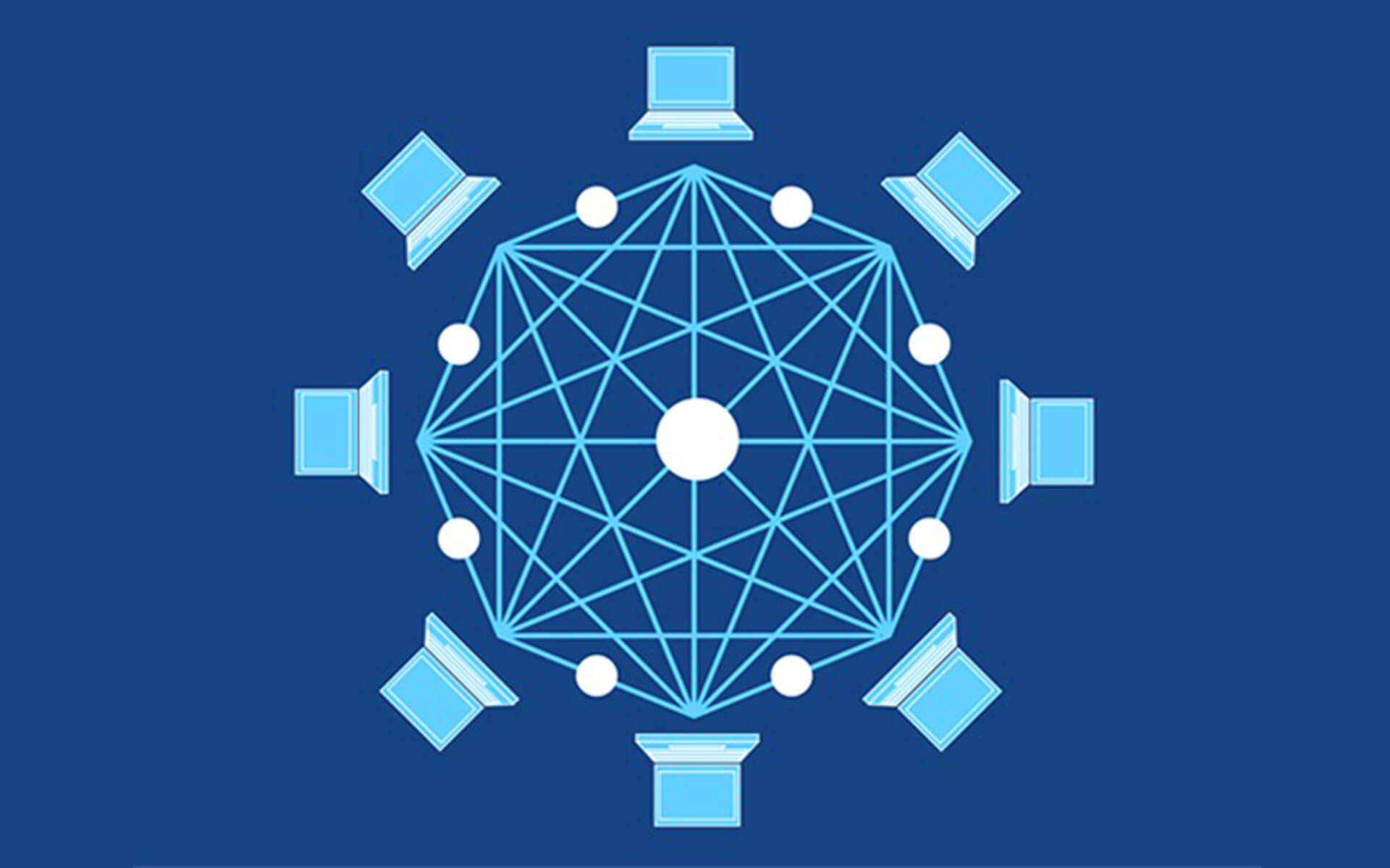
In discussing distributed ledger technology, it has been noted that there are two types of ledger technology available in the market; namely, centralised ledger technology and distributed ledger technology. The idea behind distributed ledger technology is to use a global computer network (LAN), instead of a local one, to facilitate global business transactions. To date, this system is commonly known as the distributed ledger technology. A centralised bank, which uses the system to manage its financial transactions, would also require a highly efficient and secure infrastructure, which can be accessed by all its customer's computers.
The other option, known as the distributed ledger technology, enables two parties involved in a transaction to agree on the information contained in a document, by having each participant individually or collectively sign the agreement. This facility is called open source cryptography. This system makes use of mathematics to provide trust among the participants in a transaction. The decision of each participant is subject to the rules of the distributed ledger. However, this system does not allow two parties involved in a transaction to make independent decisions regarding the funds they have transferred.
One such distributed ledger technology is bitcoins. It is believed to be one of the latest breakthroughs in information and financial transaction technologies. The major appeal of bitcoins lies in its ability to preserve the integrity and decentralised nature of the ledger system, while introducing transparency and fungibility into the monetary system. Hence, the transfer of currency from one address to another via the internet is fully traceable, as tracked by the public key that has been embedded in the digital currency.
Another distributed ledger technology that has gained momentum recently is the asynchronous byzantine fault-tolerant (Abfts) consensus algorithm, a compact and self-contained tool for the efficient management of electronic data. The compact design of Abfts minimizes the risk of system crashes that are often the result of extensive reporting. In addition, the Abfts storage format is highly efficient and flexible, making it suitable for both batch and streaming workloads. A major advantage of Abfts is that it can scale up to large volumes of data easily, thanks to its advanced read/write capabilities.
Consensus algorithms are another important aspect of distributed ledger technology. They provide a method of ensuring that no single party controls the transaction data. In most cases, this is achieved through a process of "consensus", which is achieved by the majority of participants in the system. Consensus algorithms ensure that all the transactions are carried out in the right way. The algorithm is usually specified in a formal specification that is agreed upon by the various stakeholders in the system. This ensures that the algorithm will evolve only if the needs of its real-world users are correctly evaluated.